[OS] Message Queue
IPC를 위한 방법은 크게 6가지가 있다.
- Pipe
- FIFO
- Message Queue
- Shared Memory
- Semaphore
- Socket
Pipe나 FIFO는 file descriptor를 이용해서 통신하기 때문에 virtual file system에 속한다. Message queue, shared memory, semaphore는 key값을 통해서 통신한다.
기본적으로 message queue는 permission이 R/W는 존재하며 X가 없다.
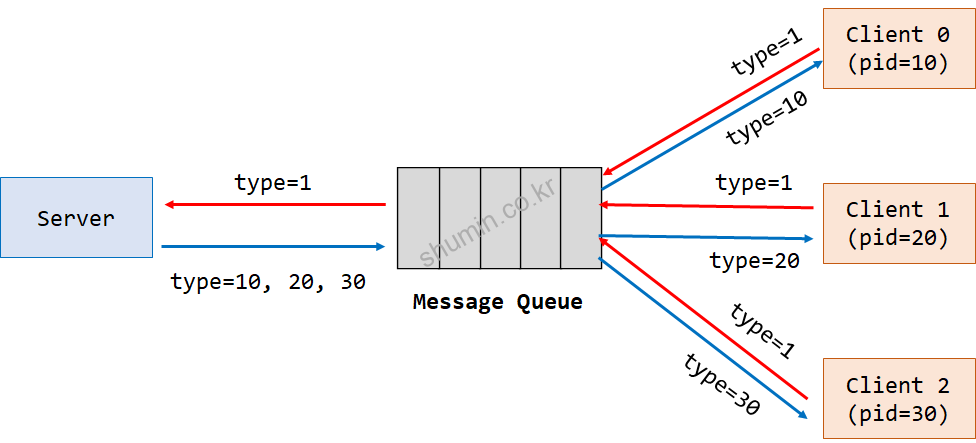
기본적으로 내부는 singlely-linked list로 구성된다. Pipe와 큰 차이점은 타입을 줄 수 있다. Message를 전송할 때 반드시 타입을 명시해야한다. Message queue의 구조는 다음과 같다.
struct msqid_ds {
struct ipc_perm msg_perm; /* Ownership and permissions */
time_t msg_stime; /* Time of last msgsnd(2) */
time_t msg_rtime; /* Time of last msgrcv(2) */
time_t msg_ctime; /* Time of last change */
unsigned long __msg_cbytes; /* Current number of bytes in
queue (nonstandard) */
msgqnum_t msg_qnum; /* Current number of messages
in queue */
msglen_t msg_qbytes; /* Maximum number of bytes
allowed in queue */
pid_t msg_lspid; /* PID of last msgsnd(2) */
pid_t msg_lrpid; /* PID of last msgrcv(2) */
};
Message queue에 전송되는 데이터 구조는 다음과 같다.
struct {
long data_type; // must have variable
int data_num;
char data_buff[BUFF_SIZE];
}
참고로 message queue를 사용하는데 필요한 header file들은 다음과 같다.
#include <sys/msg.h> #include <sys/ipc.h> #include <sys/types.h>
msgget
Message queue를 만들 때 사용하는 함수다.
int msgget(key_t key, int msgflg);
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
| key_t key | Message queue를 얻어올 때 사용하는 key 값 |
| int msgflg | IPC_CREAT: key에 해당하는 큐가 있다면 큐의 식별자를 반환하며, 없으면 생성 IPC_EXCL: key에 해당하는 큐가 없다면 생성하지만 있다면 -1을 반환하고 복귀 |
| Return | Description |
|---|---|
| -1이 아닌 값 | Message queue ID |
| -1 | 실패 |
msgctl
Message queue를 관리할 때 쓰는 함수다. Message queue를 지울 때도 사용된다.
int msgctl ( int msqid, int cmd, struct msqid_ds *buf )
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
| int msqid | 목표하는 message queue ID |
| int cmd | Command 종류 IPC_STAT: message queue의 현재 상태를 buf에 저장 IPC_SET: message queue의 상태를 buf 값으로 변경합니다. 그러나 모든 정보는 안되고 msg_perm과 msg_qbytes 내용만 변경할 수 있음 IPC_RMID: message queue를 삭제합니다. 이럴 때에는 buf가 필요 없으므로 buf 를 0 으로 지정 |
| struct msqid_ds *buf | Message queue 정보를 받을 버퍼 |
| Return | Description |
|---|---|
| 0 | 성공 |
| -1 | 실패 |
msgsnd
Message를 전달할 때 쓰는 함수다.
int msgsnd(int msqid, const void *msgp, size_t msgsz, int msgflg);
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
| int msqid | 목표하는 message queue ID |
| const void *msgp | 전송할 데이터 |
| size_t msgsz | 전송할 데이터 크기 |
| int msgflg | 동작 옵션 0: message queue에 공간이 생길 때 까지 대기 IPC_NOWAIT: message queue에 여유 공간이 없다면 바로 -1 로 복귀 |
| Return | Description |
|---|---|
| 0 | 성공 |
| -1 | 실패 |
msgrcv
Message를 받는데 사용하는 함수다. 참고로 argument 중 첫 번째 인자인 msgid는 수신된 데이터 중 구조체의 첫 번째 멤버 변수와 비교하는데 사용된다.
ssize_t msgrcv(int msqid, void *msgp, size_t msgsz, long msgtyp, int msgflg);
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
| int msqid | 목표하는 message queue ID |
| void *msgp | 전송할 데이터 |
| size_t msgsz | 전송할 데이터 크기 |
| long msgtyp | Message queue에 있는 데이터 중 어떤 값을 읽을 지에 대한 옵션 0: message queue에 자료가 있다면 첫 번째의 자료를 읽음 양수: 양수로 지정한 값과 같은 data_type의 자료 중 첫 번째를 읽어 들입니다. 음수: 음수 값을 절대 값으로 변경하고, 이 절대값과 같거나 보다 제일 작은 data_type의 자료를 구합니다. Message queue에 data_type 이 1, 5, 15 이고 -10을 지정했다면 1의 데이터를 구함 |
| int msgflg | 읽어 들이는 옵션 0: 옵션 사용하지 않음 IPC_NOWAIT: message queue에 메시지가 없다면 기다리지 않고 -1 로 복귀 MSG_NOERROR: message queue에 있는 자료가 준비된 데이터 크기보다 크다면 초과 부분을 잘라 내고 읽어 들일 수 있는 부분만 담아 전달. 이 옵션이 없다면 메시지 큐에 자료가 있다고 하더라도 -1 로 실패 |
| Return | Description |
|---|---|
| 0 | 성공 |
| -1 | 실패 |
Example
5000번 Message queue를 생성해서 타입 번호 1번 message를 전송하는 프로그램이다. Client 코드는 echo client로 구현되어있다.
// msglib.c
#include "msglib.h"
int CreateMQ(long key) {
return( msgget(key, IPC_CREAT | 0777) );
}
int OpenMQ(long key) {
return( msgget(key, 0) );
}
long SendMQ(int qid, long mtype, MSG_t msg) {
int st;
msg.to_mtype = mtype;
msg.fm_mtype = getpid();
/* msgsnd() : Return 0 if OK, -1 on error */
st = msgsnd(qid, &msg, (sizeof(MSG_t)-sizeof(long)), IPC_NOWAIT);
if(st < 0)
return -1L;
return msg.fm_mtype;
}
long RecvMQ(int qid, long mtype, MSG_t *msg) {
int st;
/* msgrcv() : Return recv bytes if OK, -1 on error */
st = msgrcv(qid, msg,sizeof(MSG_t)- sizeof(long),
mtype, IPC_NOWAIT);
if(st < 0)
return -1L;
return msg->fm_mtype;
}
int GetFreeSizeMQ(int qid, long *freesize) {
int rtn;
struct msqid_ds stat_q;
if(qid<0)
return -1;
/* msgctl() : Return 0 if OK, -1 on error */
rtn = msgctl(qid,IPC_STAT,&stat_q);
if(rtn < 0)
return -1;
*freesize = stat_q.msg_qbytes - stat_q.msg_cbytes;
return rtn;
}
int RemoveMQ(int qid) {
return(msgctl(qid, IPC_RMID, 0));
}
// msglib.h
#include <unistd.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
typedef struct msg_q {
long to_mtype;
long fm_mtype;
char mtext[100];
} MSG_t;
int CreateMQ( long key_t );
int OpenMQ( long key_t );
long RecvMQ( int qid, long mtype, MSG_t *msgbuf );
long SendMQ( int qid, long mtype, MSG_t msgbuf );
int GetFreeSizeMQ(int qid, long *freesize);
int RemoveMQ( int qid );
// msgserver.c
#include "msglib.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() {
int qid;
MSG_t msg;
long mtype;
qid=CreateMQ(5000);
if(qid<0) {
printf("q open fail: %d\n",errno);
return -1;
}
while(1) {
mtype = RecvMQ(qid, 1L,&msg);
if(mtype > 0)
{
if(!strcmp(msg.mtext, "exit"))
{
printf("Server Process Exit\n");
break;
}
printf("recv : %s\n",msg.mtext);
if(SendMQ(qid, mtype, msg)<0)
break;
}
}
RemoveMQ(qid);
return 0;
}
// msgclient.c
#include "msglib.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() {
int qid,st;
MSG_t msg;
qid = OpenMQ(5000);
if(qid < 0) {
printf("q open fail: %d\n",errno);
return -1;
}
while(1) {
memset(msg.mtext,'\0',100);
printf("\ninput : ");
fgets(msg.mtext, sizeof msg.mtext, stdin);
msg.mtext[strlen(msg.mtext)-1] = 0; // '\n' => '\0'
if(SendMQ(qid,1L,msg)<=0) {
printf("q send fail: %d\n",errno);
break;
}
if(!strcmp(msg.mtext, "exit")) {
printf("Client Process Exit\n");
break;
}
sleep(1);
st = RecvMQ(qid, getpid(),&msg);
if(st>0)
printf("recv : %s\n", msg.mtext);
}
return 0;
}
$ gcc msglib.c -c msglib.o $ gcc msgserver.c msglib.o -o server $ gcc msgclient.c msglib.o -o client
위 상태로 세션을 1개 더 띄워서 server와 client를 각각 띄워서 통신이 되는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
./server recv : hello // 2 ---------------------------------------------------- ./client input : hello // 1 recv : hello // 3
다수의 client가 존재 할 때 본인의 message만 받을 수 있도록 구분하는데 사용되는 ID는 각 client process의 PID를 이용한다.
Reference
- http://forum.falinux.com/zbxe/index.php?document_srl=420634&mid=C_LIB